 English
English 简体中文
简体中文  Español
Español  Português
Português  русский
русский  Français
Français  日本語
日本語  Deutsch
Deutsch  tiếng Việt
tiếng Việt  Italiano
Italiano  Nederlands
Nederlands  ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย  Polski
Polski  한국어
한국어  Svenska
Svenska  magyar
magyar  Malay
Malay  বাংলা ভাষার
বাংলা ভাষার  Dansk
Dansk  Suomi
Suomi  हिन्दी
हिन्दी  Pilipino
Pilipino  Türkçe
Türkçe  Gaeilge
Gaeilge  العربية
العربية  Indonesia
Indonesia  Norsk
Norsk  تمل
تمل  český
český  ελληνικά
ελληνικά  український
український  Javanese
Javanese  فارسی
فارسی  தமிழ்
தமிழ்  తెలుగు
తెలుగు  नेपाली
नेपाली  Burmese
Burmese  български
български  ລາວ
ລາວ  Latine
Latine  Қазақша
Қазақша  Euskal
Euskal  Azərbaycan
Azərbaycan  Slovenský jazyk
Slovenský jazyk  Македонски
Македонски  Lietuvos
Lietuvos  Eesti Keel
Eesti Keel  Română
Română  Slovenski
Slovenski  मराठी
मराठी
Specific Functions and Roles of the Three Sections Typically Found in PVC Extruder Screws
2025-07-16
Ningbo Fangli Technology Co., Ltd. is a mechanical equipment manufacturer with nearly 30 years’ experiences of plastic pipe extrusion equipment, new environmental protection and new materials equipment. Since its establishment Fangli has been developed based on user’s demands. Through continuous improvement, independent R&D on the core technology and digestion & absorption of advanced technology and other means, we have developed PVC pipe extrusion line, PP-R pipe extrusion line, PE water supply / gas pipe extrusion line, which was recommended by the Chinese Ministry of Construction to replace imported products. We have gained the title of “First-class Brand in Zhejiang Province”.
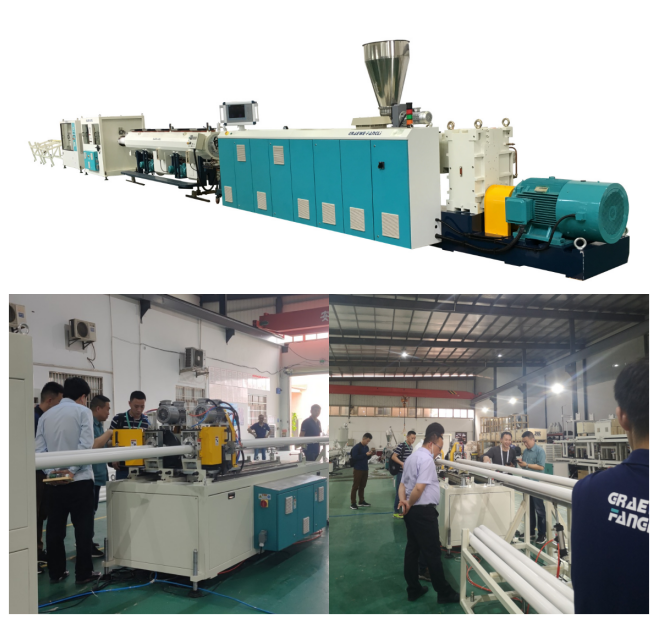

The screw of a PVC extruder is typically divided into three sections: the Feed Zone, Compression Zone, and Metering Zone. Each plays a critical role in PVC processing, working together to ensure uniform plasticization of the material, stable extrusion, and product quality. The specific functions and roles of each zone are detailed below:
1. Feed Zone
▼ Function: Responsible for steadily conveying PVC powder or pellets from the hopper to subsequent zones, while providing initial heating and compaction.
· Material Entry: This is the entry zone where the material (e.g., PVC pellets, powder) enters the extruder. Material is fed from the hopper into the feed zone, supplying raw material for the subsequent processing stages.
· Initial Mixing and Preheating: In the feed zone, the material begins to experience initial stirring and shearing from the screw rotation. Simultaneously, friction between the rotating screw and the material, as well as between material particles themselves, generates heat, leading to initial mixing and preheating. Gentle preheating is also provided by barrel heating (lower temperature, typically <120°C) to avoid premature decomposition of PVC. This facilitates the subsequent plasticization process.
· Preventing Material Backflow: The screw design in the feed zone usually features specific thread depth and pitch to effectively prevent material from flowing back into the hopper during feeding, ensuring smooth forward conveyance. Deep flight channels increase material density and expel some air, reducing bubble formation issues during later melting.
· Key Considerations: Temperature and screw speed must be controlled to prevent localized degradation of the material due to excessive frictional heat (PVC is temperature-sensitive).
· Example: In PVC pipe production, PVC pellets enter the feed zone from the hopper and begin to be stirred by the screw. Friction between pellets gradually raises their temperature, preparing them for plasticization.
2. Compression Zone (Melting Zone)
▼ Function: Transforming solid PVC into a homogeneous melt, completing plasticization, and expelling volatiles.
· Material Compression and Plasticization: After initial mixing and preheating in the feed zone, the material enters the compression zone. Here, the screw flight depth gradually decreases, and the pitch typically reduces. This subjects the material to significantly higher pressure and shear forces. Under the combined action of pressure and increasing temperature (barrel temperature rises to 160-190°C), the material begins to plasticize – transitioning from solid particles into a flowable molten state. The progressively shallower screw channels intensify shear and pressure, melting the PVC into a viscous flow state.
· Degassing/Air Removal: During compression, air trapped within the material is gradually expelled. Failure to remove air can lead to porosity or defects in the final product. The design of the compression zone helps squeeze air out of the material, ensuring uniformity and density.
· Improving Material Mixing Uniformity: Due to the screw design and operating conditions in the compression zone, the material undergoes more intense shearing and mixing action, further enhancing its homogeneity. This is crucial for consistent product quality. Shear forces promote the dispersion of additives (e.g., stabilizers, lubricants), while low-molecular-weight volatiles are expelled through vents (preventing bubbles or defects in the product).
· Key Considerations: Precise temperature control is essential to prevent PVC thermal decomposition (decomposition temperature ~200°C) while ensuring uniform plasticization.
· Example: In PVC profile production, after passing through the compression zone, the degree of PVC plasticization is greatly increased, and additives like stabilizers and lubricants become more uniformly dispersed throughout the material.
3. Metering Zone (Homogenizing Zone)
▼ Function: Further homogenizing the melt, stabilizing pressure and temperature, and ensuring consistent extrusion flow rate.
· Melt Homogenization: Material leaving the compression zone is largely plasticized. In the metering zone, however, it undergoes further homogenization. The screw flight depth and pitch design in this zone subject the melt to uniform shear and mixing, ensuring consistent melt quality. This is critical for the final product, as only a homogeneous melt guarantees stable performance of the molded item. Shallow flight channels maintain high pressure (typically 10-30 MPa), dampening fluctuations in melt temperature and viscosity, thereby enhancing extrusion stability.
· Stabilizing Melt Pressure and Temperature: A key role of the metering zone is to stabilize the melt pressure and temperature. Relatively stable melt pressure and temperature are necessary for a smooth molding process. The design of the metering zone allows the melt to reach a stable state before entering the die. It provides constant pressure to the die, ensuring product shape and dimensional accuracy (e.g., uniform pipe wall thickness).
· Filtering Impurities: In some cases, the metering zone can also incorporate a filtering function. Special screens or filters can remove impurities and unplasticized particles from the melt, further increasing its purity.
· Key Considerations: Temperature is typically slightly lower than in the compression zone (approx. 5-10°C lower) to avoid melt overheating; backflow must be prevented to ensure extrusion efficiency.
· Example: In PVC film production, the role of the metering zone is particularly vital. Only a thoroughly homogenized melt can form a uniform film during molding, guaranteeing consistent thickness and properties.
These three functional zones work synergistically. By rationally regulating the process parameters (temperature, screw speed, pressure) across all three zones, they collectively accomplish the tasks of conveying, plasticizing, mixing, and preparing the PVC material for molding. This ensures the extruder can efficiently and stably produce high-quality PVC products with consistent mechanical properties and appearance.
If you need more information, Ningbo Fangli Technology Co., Ltd. welcomes you to contact for a detailed inquiry, we will provide you with professional technical guidance or equipment procurement suggestions.



