 English
English 简体中文
简体中文  Español
Español  Português
Português  русский
русский  Français
Français  日本語
日本語  Deutsch
Deutsch  tiếng Việt
tiếng Việt  Italiano
Italiano  Nederlands
Nederlands  ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย  Polski
Polski  한국어
한국어  Svenska
Svenska  magyar
magyar  Malay
Malay  বাংলা ভাষার
বাংলা ভাষার  Dansk
Dansk  Suomi
Suomi  हिन्दी
हिन्दी  Pilipino
Pilipino  Türkçe
Türkçe  Gaeilge
Gaeilge  العربية
العربية  Indonesia
Indonesia  Norsk
Norsk  تمل
تمل  český
český  ελληνικά
ελληνικά  український
український  Javanese
Javanese  فارسی
فارسی  தமிழ்
தமிழ்  తెలుగు
తెలుగు  नेपाली
नेपाली  Burmese
Burmese  български
български  ລາວ
ລາວ  Latine
Latine  Қазақша
Қазақша  Euskal
Euskal  Azərbaycan
Azərbaycan  Slovenský jazyk
Slovenský jazyk  Македонски
Македонски  Lietuvos
Lietuvos  Eesti Keel
Eesti Keel  Română
Română  Slovenski
Slovenski  मराठी
मराठी
Pelletizing Methods for Extruders
Ningbo Fangli Technology Co., Ltd. is a mechanical equipment manufacturer with over 30 years’ experiences of plastic pipe extrusion equipment, new environmental protection and new materials equipment. Since its establishment Fangli has been developed based on user’s demands. Through continuous improvement, independent R&D on the core technology and digestion & absorption of advanced technology and other means, we have developed PVC pipe extrusion line, PP-R pipe extrusion line, PE water supply / gas pipe extrusion line, which was recommended by the Chinese Ministry of Construction to replace imported products. We have gained the title of “First-class Brand in Zhejiang Province”.
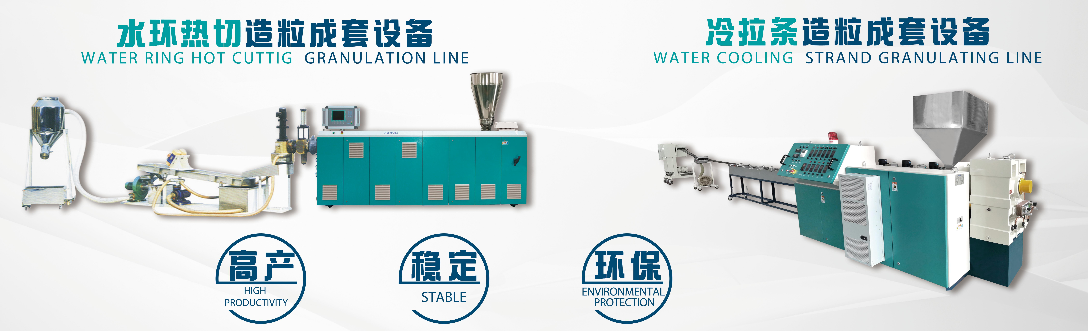
The pelletizing methods for extruders are primarily categorized into various types based on material characteristics, product requirements, and production processes. The following are detailed introductions to common pelletizing methods:
1. Die-Face Pelletizing
This method is characterized by hot cutting the material instantly as it exits the die head. It is suitable for high-viscosity and heat-sensitive materials and requires cooling with water or air.
· For example, the Water Ring Pelletizing Process: After the material is extruded into strands from the die head, it immediately enters the cutting zone formed by high-speed rotating blades and the die face. Simultaneously, it is encased in circulating water for cooling. The pellets and water then enter a dewatering system for separation.
Advantages: Rapid cooling, suitable for heat-sensitive materials, avoiding high-temperature degradation; uniform pellet size and regular shape; high degree of automation and production efficiency, suitable for continuous production.
Disadvantages: Requires a supporting water circulation system, leading to higher equipment investment and energy consumption; high water quality requirements, necessitating regular maintenance to prevent clogging from scale.
Widely used in pelletizing plastics such as polyolefins, nylon, and polyester.
· Another example is the Air Pelletizing Process: The extruded material is directly cut by high-speed rotating blades in the air. The pellets are conveyed to the cooling and screening system either by their own momentum or with the assistance of an air stream.
Advantages: No water circulation needed, simpler equipment, lower cost; suitable for low-viscosity, non-sticky materials, avoiding potential contamination from water.
Disadvantages: Relies on air for cooling, which is less efficient and may cause pellets to stick together; requires high blade precision; pellet size uniformity is slightly inferior to water ring pelletizing.
Suitable for certain rubbers, waxes, low-melting-point polymers, or materials sensitive to moisture.
2. Strand Pelletizing
This method is characterized by first cooling and solidifying the extruded strands before cutting them with blades. It is suitable for medium to low viscosity materials and offers high process flexibility.
· For example, the Water-Cooled Strand Pelletizing Process: The material is extruded into strands from the die head, then solidified by passing through a water cooling tank, stretched to a uniform diameter by a haul-off unit, and finally cut into pellets by a pelletizer.
Advantages: Simple equipment, low investment cost, suitable for small-scale production or pilot lines; strong adaptability to different materials, allowing control of strand diameter and pellet length by adjusting the haul-off speed.
Disadvantages: Lower production efficiency, requires more manual intervention; pellet surface might develop water marks from contact with the water tank, potentially affecting appearance or performance.
Commonly used for engineering plastics, modified plastics, and some rubber products.
· Another example is the Air-Cooled Strand Pelletizing Process: The extruded strands are solidified via an air cooling tunnel or natural air cooling before being cut.
Advantages: No water tank required, preventing contact between material and water, suitable for moisture-sensitive materials.
Disadvantages: Slow cooling speed, low production efficiency, only applicable for low-output scenarios.
Used for moisture-sensitive resins.
If you need more information, Ningbo Fangli Technology Co., Ltd. welcomes you to contact for a detailed inquiry, we will provide you with professional technical guidance or equipment procurement suggestions.



